While CBD and THC are the most popular compounds in the industry, CBN is one of the most well known minor cannabinoids known for its ability to promote maximum wellness. CBN was actually the first cannabinoid ever extracted and has been the subject of decades of research.
Cannabinoids are chemicals found in cannabis. These chemical compounds contribute to the varying psychoactive and medicinal effects of cannabis. The most well-known cannabinoid is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is the plant’s main psychoactive compound. Cannabidiol (CBD) is the second most prevalent cannabinoid found in cannabis. While THC and CBD are now well known, there are over 100+ different cannabinoids that can be found in cannabis.
Less abundant cannabinoids known as “minor cannabinoids” include CBN, CBG, CBC, THCV, CBL, CBDV to name a few. Like CBD and THC, minor cannabinoids can be found at varying levels in cannabis and offer unique medicinal benefits. Therefore, if you’re interested in how a specific cannabis strain or product will affect you or how to formulate a cannabis product for targeted results, learning about these different cannabinoids is an essential first step.
In this article, we will focus on the benefits and uses of the minor cannabinoid CBN (cannabinol).
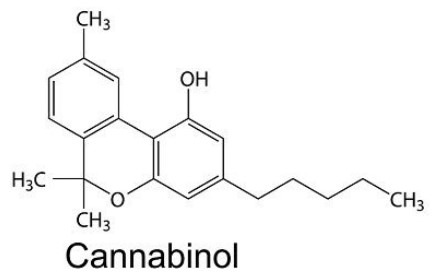
What is CBN?
CBN was one of the first cannabinoids to be isolated by scientists in the 1930s.1 THCA (the natural acid form of THC) converts into CBNA through oxidation and degradation processes that occur once the cannabis plant has been harvested and stored for some time. Simply speaking, when THCA is heated and exposed to oxygen or ultraviolet light, it can both decarboxylate into its non-acidic form THC or convert into CBNA. CBNA can then similarly decarboxylate under similar conditions to CBN. CBN is mildly psychoactive in relation to THC and is often found in trace amounts within plant matter that has been aged.
Researchers studied the feeding patterns of rats after administering cannabinol. What they found was that rats treated with CBN were quicker to eat, ate more and for longer durations of time. The research concluded the less popular cannabinoid was a viable nonpsychoactive appetite stimulant.
A 2006 study found that CBN and several other cannabinoids have the ability to control the growth of cancer cells. CBN was specifically able to control a type of lung tumor called Lewis carcinoma.
Back in 1974, researchers found that THC, CBD and CBN all had anticonvulsant properties but potency-wise, CBN is less active than the other two.
In 2002, Swedish researchers at the Department of Clinical Pharmacology at Lund University Hospital found out cannabinol and THC activate the same pain pathways.
How does CBN work in the body?
Cannabinoids, like CBN, operate in the human body by acting on the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), which is made up of a series of receptors that promote homeostasis and are believed to regulate a variety of human functions including mood, sleep, appetite, memory, and pain. The ECS has two central receptors known as CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is found in the highest occurrence throughout the brain, central nervous system (CNS), lungs and dermis (skin). When activated the CB1 receptor triggers biochemical responses within the cells to modulate physiological responses such as mood, memory, and pain perception. In contrast, CB2 receptors are primarily found throughout the internal organs, blood and bone marrow. CB2 receptors therefore have a direct impact on modulation of the body’s innate immune system.
The body naturally produces its own cannabinoids, which are known as endocannabinoids (from the Greek word Endo, meaning “from within”). Plants similarly produce their own cannabinoids, known as phytocannabinoids (from the Greek word phyto, meaning “from plants”). All of these cannabinoids bind to the same receptors within the human body (same for animals) allowing phytocannabinoids to be such an excellent source to acquire these critical molecules for health supplementation. Because so many people suffer from certain conditions that are associated with Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome (CEDS), cannabis supplementation studies have shown potential to be a very effective means of managing such conditions.
CBN is a partial agonist of the CB2 receptor within the ECS and may also interact with the CB1 receptor but at a much lower affinity, than THC does.2 This means CBN won’t alter your state of consciousness to the extent of psychoactive intoxication that THC induces, however, it does trigger a response (particularly in the presence of THC) that operates as a heavy sedative. For this reason CBN is sought after for its ability to aid in sleep and combat insomnia. In addition to its popularity as an effective sleep aid, CBN has been researched for its analgesic, antibacterial, and appetite stimulant properties.
CBN uses & benefits
- The most well-known benefit of CBN is its sedative properties. Many of the relaxing and soothing effects that are associated with cannabis consumption are believed to be a result of either CBN or terpene levels, or a combination of the two. These properties can help promote sleep and reduce problems associated with sleep disorders such as sleep apnea and insomnia.
- CBN has been shown to exert positive appetite stimulating effects in rats3
- This indicates that it can potentially be used as an appetite stimulant for those suffering through medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
- CBN can decrease intra-ocular pressure and is being looked into with potential abilities to support those with glaucoma.
- Similar to other cannabinoids, CBN may show promise in cancer treatment by limiting tumor growth.4
- CBN’s similar properties to THC, as an effective analgesic to reduce pain related to inflammation, position it to be used in pain management treatments.
- CBN displays anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, which supports evidence that there is potential that CBN could help with certain skin conditions such as psoriasis and mild burns through topical application.
- Research has indicated CBN has the ability to slow down the onset of symptoms caused by ALS in mice, proving it to be a potential beneficial treatment for this progressive, degenerative disease.5
CBN & the entourage effect

There is evidence that the sedative effects of CBN can be amplified and work best when paired with THC. CBD Global has been conducting in-depth research on CBN for over a year with a focus on specific formulation requirements to allow CBN to activate without the use of THC. (More on this research to come!)
It is important to note that CBD displays properties of a negative allosteric modulator on the CB1 receptor within the ECS.6 This means that the addition of CBD into any products also containing CBN, may reduce effectiveness and lessen its sedative properties if not formulated properly. Even trace amounts of CBD can limit the amplifying effects of THC on CBN. This is because the receptor altering properties of CBD bind to receptors in the ECS in place of CBN or THC molecules that would otherwise bind and complement one another.
The entourage effect suggests that there are often added benefits to using the many compounds found in cannabis in conjunction with one another. However, this reduced effect seen when CBD is included in CBN products suggests that this term is widely used and often misunderstood. Although more research is needed to support evidence of the entourage effect, in the case of CBN products, the effects of pairing certain cannabinoids together can actually lead to a decrease in effectiveness depending on the formulation.
Studies on male volunteers illustrated that doses of CBN did not provide the psychoactive effects that THC did. The study also noted that subjects felt more “drugged, drunk, dizzy and drowsy” when it was combined to THC. They concluded that, “CBN increases the effect of THC on some aspects of physiological and psychological processes, but that these effects are small.”
On the other hand, some studies didn’t note as much of a synergetic effect when combined with THC. One study found the combination of THC and CBN did nothing to change “the quality, intensity, or duration of the effects of THC alone.”
Research has also shown that cannabinol is capable of slowing the onset of symptoms from ALS. Additional research shows cannabinol has antibacterial capabilities as a topical. The study showed “potent activity against MRSA.” Experimental and preclinical studies have shown topical cannabinol’s potential for treating skin conditions like psoriasis or burns.
Studies on male volunteers illustrated that doses of CBN did not provide the psychoactive effects that THC did. The study also noted that subjects felt more “drugged, drunk, dizzy and drowsy” when it was combined to THC. They concluded that, “CBN increases the effect of THC on some aspects of physiological and psychological processes, but that these effects are small.”
On the other hand, some studies didn’t note as much of a synergetic effect when combined with THC. One study found the combination of THC and CBN did nothing to change “the quality, intensity, or duration of the effects of THC alone.”
Research has also shown that cannabinol is capable of slowing the onset of symptoms from ALS. Additional research shows cannabinol has antibacterial capabilities as a topical. The study showed “potent activity against MRSA.” Experimental and preclinical studies have shown topical cannabinol’s potential for treating skin conditions like psoriasis or burns.
Where Can You Find CBN (Cannabinol)?
Up until lately, the only place you could find CBN was in extremely small concentrations of certain weed strains. The concentrations in flowers are typically 1 percent or less. Until recently, extracts have either focused on isolating THC or CBD. Fortunately, less common cannabinoids like delta 8 THC are starting to be isolated and extracted. Cannabinol is a little different. Since it exists in such small quantities in flower, we haven’t seen CBN in a concentrated form like with THC, delta 8 or THC-O-acetate. However, with Cannabinol a little goes a much longer way than it would with equal quantities of THC or CBD.
Mary’s Medicinals Cannabinol Capsules is one form that is easy to ingest for any type of patient suffering from sleep-deprivation. Capsules make it easy to know exactly how much you’re consuming in a single sitting. Mary’s Medicinals also has high-cannabinol transdermal patches.
For patients that don’t like patches or swallowing pills, SpOILed Patients Collective makes a high-dose CBN drink called Hornet Hibernate. SpOILed says their Cannabinol drink contains a wide spectrum of cannabinoids including CBC, CBD and small amounts of THC for the entourage effects. From their experience with the Hornet Hibernate, Cannabinol amplifies the effects of THC. Smoking a few bowls on top of a teaspoon will “send you to the moon,” SpOILed tells us. Each bottle contains about 10 to 12 percent CBN and you’ll only need a teaspoon without the smoke to get a solid nights sleep, illustrating how far a little goes. They’re working on versions with delta-8 THC or delta-9 THC for patients that need them.
The Hornet Hibernate is approved by the veterans of the Weed For Warriors Project. SpOILed says the combination of CBD and CBN has been helping veterans to get off of fentanyl patches and curb opiate addictions. They claim the healing properties of the CBD combined with the sedative effects of CBN have helped many of their patients through hard times.
The thing that sets cannabinol apart from the other cannabinoids in weed is the strong sedative ability. It can also stimulate appetite and curb anxiety without the side effects of a medication like a valium. The research on cannabinol, especially on humans is currently lacking. As more research is conducted on CBN, we may find even more uses for it. Most of the reported effects don’t have much to back them up yet.

So, to make a high CBN tincture at home I put the unheated weed in an open glass jar in a window exposed to sunlight? For how long?